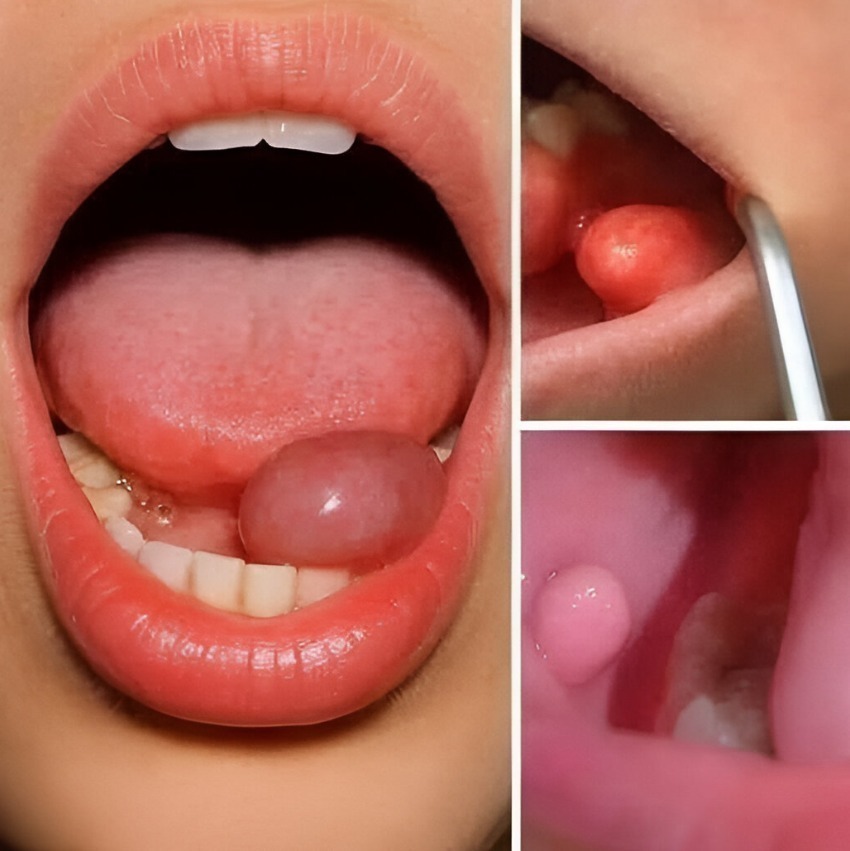
Here’s a clear and thorough breakdown of mouth cancer cysts and their causes:
1. What Are Mouth Cancer Cysts?
- The term “cyst” usually refers to a sac or lump filled with fluid, air, or semi-solid material.
- In the context of mouth cancer, a cyst-like lesion may appear as:
- A persistent lump in the mouth, gums, or jaw
- A swelling under the tongue, cheek, or palate
- Sometimes painless at first, but may become tender as it grows
⚠️ Not all oral cysts are cancerous. Most cysts in the mouth are benign (non-cancerous), but some can indicate malignancy.
2. Common Causes / Risk Factors
Mouth cancer cysts usually develop due to a combination of environmental, lifestyle, and biological factors:
a) Tobacco Use
- Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or using chewing tobacco increases risk of oral cancers.
- Tobacco toxins can cause abnormal cell growth, sometimes forming cyst-like lesions.
b) Alcohol Consumption
- Heavy drinking, especially combined with tobacco, multiplies the risk.
- Alcohol irritates the lining of the mouth, making it more susceptible to cancer.
c) HPV Infection
- Certain strains of Human Papillomavirus (HPV), especially HPV-16, are linked to oral cancers.
- Infection can cause abnormal cells that may form cysts or lumps.
d) Chronic Irritation
- Ill-fitting dentures, sharp teeth, or constant trauma to the mouth may trigger abnormal growth.
e) Genetic & Cellular Changes
- Mutations in oral cells can lead to uncontrolled growth, forming cysts or tumors.
- Family history of cancer can slightly increase risk.
f) Other Risk Factors
- Poor oral hygiene
- Diet low in fruits and vegetables
- Weakened immune system
3. Warning Signs
You should get checked by a dentist or doctor if you notice:
- A persistent lump or thickening in the mouth or jaw
- Pain, tenderness, or numbness
- Red or white patches that don’t heal
- Unexplained bleeding
- Difficulty swallowing or moving your tongue
4. Diagnosis & Treatment
- Diagnosis: Usually involves a dental exam, imaging (X-ray/CT), and biopsy to confirm if it’s cancerous.
- Treatment: Depends on type and stage, may include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. Early detection greatly improves outcomes.
💡 Key takeaway: Not every cyst in the mouth is cancer. But persistent, unusual lumps or sores should always be checked by a professional. Early detection is critical.
If you want, I can make a simple table showing the differences between benign mouth cysts vs. cancerous cysts, so you can quickly spot warning signs. Do you want me to do that?